There are many different types of sutures grouped by several different characteristics. Understanding these characteristics allows for ideal suture selection.
The main factors used to classify sutures types are:
1.Absorbable vs. Non-absorbable
2.Synthetic vs. Natural
3.Monofilament vs. Multifilament
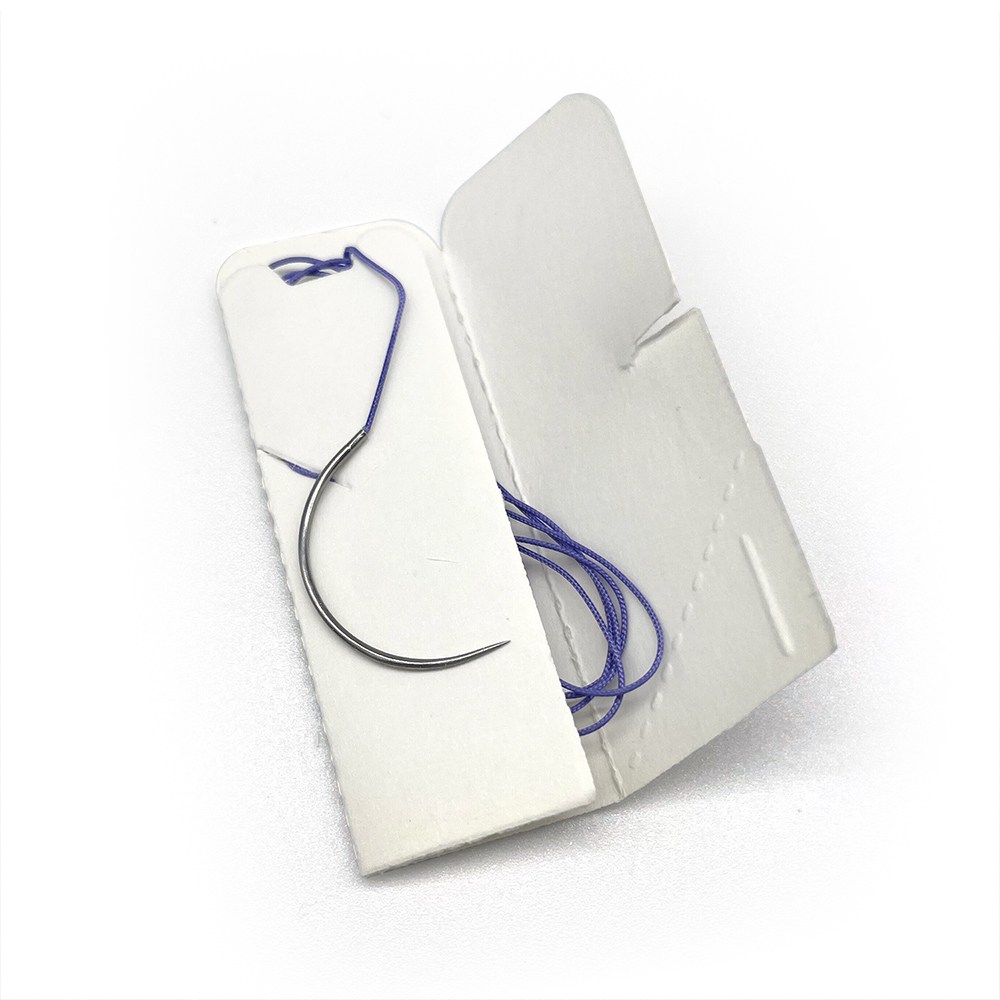
The first main suture category is absorbable versus non-absorbable sutures. Sutures are considered absorbable if they lose most of their tensile strength over variable periods ranging from a few weeks to several months. Absorbable sutures are often employed for deep temporary closure until the tissues heal or when it is not easy to remove them otherwise. In this fashion, they are useful for approximating edges of tissue layers, closing deep spaces or defects, and facilitating wound healing as part of a multi-layered closure.When used superficially, they can have more inflammation, which can lead to more scarring. If using absorbable sutures superficially, the recommendation is that a rapidly absorbing suture is employed.
Examples:
1.Natural Sutures: Plain Catgut, Chromic Catgut, Silk
2.Synthetic Sutures: Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl), Polydioxanone (PDS), Nylon , Polypropylene (Prolene, Surgipro)
3.Absorbable Sutures: Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl), Polydioxanone (PDS)
4.Non-absorbable Sutures: Nylon , Polypropylene (Prolene)
5.Monofilament Sutures: Nylon , Polypropylene (Prolene), Polydioxanone (PDS), Poliglecaprone 25 (Monocryl)
6.Multifilament Sutures: Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl), Silk, Nylon, Polyester
Post time: 7月-26-2023