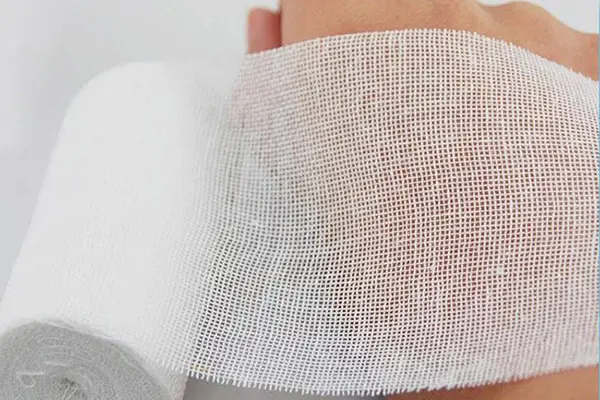
Understanding Medical Gauze Fabric
In the realm of medical care, gauze stands as an indispensable tool, serving a multitude of purposes from wound dressings to surgical sponges. This versatile fabric, woven from cotton or synthetic fibers, is characterized by its absorbent and breathable nature, making it ideal for various applications in wound management and general medical procedures.
Types of Medical Gauze Fabric
Medical gauze fabric encompasses a diverse range of types, each tailored to specific applications and wound conditions. Let's delve into the key types and their distinct characteristics:
-
Plain Gauze: This basic form of gauze is a lightweight, open-weave fabric, commonly used for dressing minor wounds, covering surgical incisions, and providing general wound protection.
-
Absorbent Gauze: As the name suggests, absorbent gauze features a higher thread count and a denser weave, making it exceptionally effective in absorbing fluids and exudates from wounds. This type is ideal for managing moderate to heavily draining wounds.
-
Non-Adherent Gauze: This specialized gauze is coated with a thin layer of silicone or polyethylene, preventing it from sticking to the wound surface. Non-adherent gauze is particularly useful for dressing delicate wounds, burns, and skin grafts, minimizing pain and tissue damage during dressing changes.
-
Impregnated Gauze: This type of gauze incorporates various medications or antiseptic agents into its fibers, providing localized treatment directly to the wound site. Impregnated gauze is commonly used for treating infected wounds, promoting healing, and reducing the risk of further infections.
-
Fenestrated Gauze: This unique gauze features perforated holes or slits, allowing for direct wound observation and drainage while maintaining wound protection. Fenestrated gauze is particularly useful for dressing wounds with drainage tubes or for monitoring wound healing progress.
-
Conforming Gauze: This type of gauze possesses a flexible and stretchy nature, enabling it to conform to the contours of the body, providing a snug and secure fit. Conforming gauze is ideal for dressing wounds on areas with movement or irregular shapes.
Gauze Sponges: A Versatile Tool
Gauze sponges, also known as surgical sponges or laparotomy sponges, are essential components of surgical procedures. These sponges, made from absorbent gauze, are used to absorb blood and fluids during surgery, maintaining a clear operating field and facilitating surgical maneuvers. Gauze sponges come in various sizes and shapes to suit different surgical needs.
Medical Gauze Sponges Softness
The softness of medical gauze fabric is a crucial factor in ensuring patient comfort and preventing wound irritation. Soft gauze is gentler on delicate skin and reduces the risk of abrasions or discomfort during dressing changes. Gauze softness is influenced by the type of fibers used, the weave pattern, and the manufacturing process.
Choosing the Right Medical Gauze
The selection of the appropriate medical gauze depends on the nature of the wound, the exudate level, and the desired treatment approach. For minor wounds, plain gauze may suffice. For moderate to heavily draining wounds, absorbent gauze is preferred. For delicate wounds or skin grafts, non-adherent gauze is essential. Impregnated gauze is utilized for treating infected wounds. Fenestrated gauze facilitates wound observation and drainage. Conforming gauze provides a snug fit for wounds on irregular surfaces.
Conclusion
Medical gauze fabric plays a pivotal role in wound management and surgical procedures. Its versatility, absorbency, and breathability make it an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals. Understanding the different types of medical gauze and their unique properties empowers healthcare providers to select the most appropriate gauze for each patient's needs.
Post time: 11月-06-2023