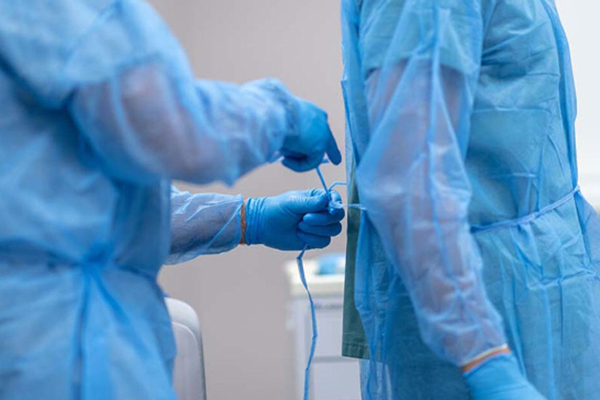
In the fight against infectious diseases, personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in safeguarding both healthcare workers and patients. Among the various types of PPE, medical isolation gowns are essential for preventing the spread of infections in healthcare settings. To ensure that these gowns provide adequate protection, they must meet specific standards and guidelines. Understanding these standards is crucial for healthcare facilities when selecting the appropriate gowns for their staff.
Purpose of Medical Isolation Gowns
Medical isolation gowns are designed to protect healthcare workers and patients from the transmission of infectious agents, especially in environments where exposure to bodily fluids, pathogens, or other contaminants is likely. These gowns create a barrier between the wearer and potential sources of infection, reducing the risk of cross-contamination. Isolation gowns are used in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and laboratories, and are particularly important during outbreaks of infectious diseases.
Key Standards for Medical Isolation Gowns
Several organizations have established standards for medical isolation gowns to ensure their effectiveness and safety. These standards address various aspects of gown performance, including material quality, design, and fluid resistance.
1. AAMI Levels of Protection
The Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) has developed a classification system that categorizes medical gowns into four levels based on their fluid barrier performance. This classification is widely recognized and used in healthcare settings.
- Level 1: Offers the lowest level of protection, suitable for minimal risk situations such as basic care or standard hospital visits. Level 1 gowns provide a light barrier against fluid exposure.
- Level 2: Provides a higher level of protection than Level 1, suitable for low-risk situations such as blood draws or suturing. These gowns offer a moderate barrier against fluids.
- Level 3: Designed for moderate-risk situations, such as inserting an intravenous (IV) line or working in the emergency room. Level 3 gowns provide a higher level of fluid resistance and are appropriate for use in environments where exposure to bodily fluids is likely.
- Level 4: Offers the highest level of protection, suitable for high-risk situations such as surgery or dealing with large amounts of fluid. Level 4 gowns provide a complete barrier to fluids and are typically used in operating rooms or during high-exposure procedures.
2. ASTM Standards
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) sets standards for the material properties of medical isolation gowns, including their resistance to fluid penetration. ASTM standards, such as ASTM F1670 and ASTM F1671, test the ability of gown materials to resist penetration by synthetic blood and blood-borne pathogens, respectively. These standards are essential for determining the effectiveness of gowns in protecting against contamination.
3. FDA Guidelines
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates medical isolation gowns as Class II medical devices. The FDA requires that manufacturers provide evidence that their gowns meet specific performance standards, including fluid resistance, durability, and breathability. Gowns that meet these requirements are labeled as “surgical” or “non-surgical,” depending on their intended use. Non-surgical gowns are generally used for patient care activities, while surgical gowns are used in sterile environments.
Materials and Design Considerations
Medical isolation gowns must be made from materials that provide adequate protection while maintaining comfort and breathability. Common materials include spun-bond polypropylene, polyethylene-coated polypropylene, and SMS (spunbond-meltblown-spunbond) fabric. These materials are chosen for their ability to resist fluid penetration while allowing air to circulate, preventing the wearer from overheating.
The design of the gown is also critical to its effectiveness. Medical isolation gowns typically feature long sleeves with elastic cuffs, full front coverage, and ties or Velcro closures at the back to ensure a secure fit. The gowns should be easy to put on and remove, minimizing the risk of contamination during doffing.
Quality Assurance and Testing
To ensure that medical isolation gowns meet the required standards, they must undergo rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. Manufacturers conduct tests to evaluate the gown’s fluid resistance, tensile strength, and seam integrity. These tests help verify that the gowns can withstand the demands of healthcare environments and provide reliable protection.
Conclusion
Medical isolation gowns are a critical component of PPE in healthcare settings, providing a barrier against infectious agents and reducing the risk of cross-contamination. To ensure their effectiveness, these gowns must meet specific standards set by organizations such as AAMI, ASTM, and the FDA. By understanding and adhering to these standards, healthcare facilities can select the appropriate isolation gowns for their staff, enhancing safety and protecting both healthcare workers and patients from infection. As the demand for high-quality PPE continues to grow, it is essential to prioritize gowns that meet these rigorous standards, ensuring that they perform as needed in the most challenging healthcare environments.
Post time: 9月-09-2024