Unveiling the Secrets of Suture Needles: The Ideal Partners for Skin Closure
In the realm of surgical procedures, suture needles play an indispensable role, serving as the delicate guides that usher sutures through tissues, facilitating wound closure and promoting healing. These slender, tapered tools, often made from stainless steel or other durable materials, are carefully selected to match the specific suture material and the intended application. Understanding the intricacies of suture needles is crucial for surgeons, nurses, and anyone involved in the healing process.
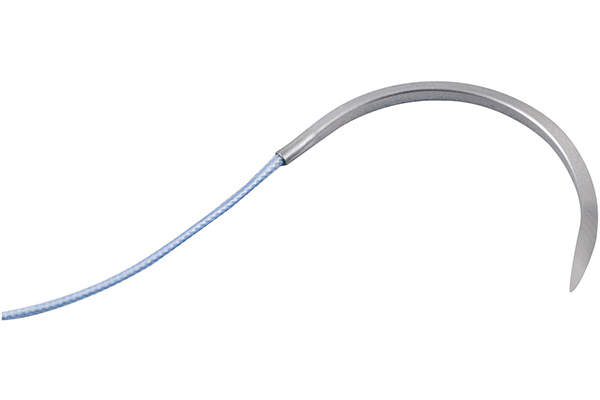
The Anatomy of a Suture Needle: A Symphony of Precision and Form
Suture needles, despite their seemingly simple appearance, are meticulously designed to optimize their performance:
-
Point: The point of the needle is the initial entry point into the tissue. Its shape and sharpness vary depending on the type of tissue to be penetrated.
-
Body: The body of the needle provides the structural support for the suturing process. Its diameter and curvature are tailored to the specific suture material and the desired needle manipulation.
-
Swaged or Eye: The needle's end features either a swaged or eye design. Swaged needles have a smooth, rounded end, while eye needles have a small opening to attach the suture.
Choosing the Right Suture Needle for Skin Closure: A Delicate Balance
The selection of the appropriate suture needle for skin closure hinges on several factors:
-
Skin Thickness: The needle's diameter should match the thickness of the skin being sutured. Too thin a needle may bend easily, while too thick a needle may cause excessive tissue trauma.
-
Wound Type: The needle's shape and point design are dependent on the type of wound. Reverse cutting needles are commonly used for skin closure, while taper-point needles are suitable for delicate tissues.
-
Suturing Technique: The needle's flexibility and curvature should complement the preferred suturing technique. Straight needles are versatile for various techniques, while curved needles offer better access in recessed areas.
Common Suture Needle Types for Skin Closure:
-
Reverse Cutting Needle: This versatile needle features a triangular point with two cutting edges, making it suitable for a wide range of skin closure techniques.
-
Taper Point Needle: This needle features a gradually tapering point, ideal for delicate tissues or areas where minimal tissue disruption is desired.
-
Circle Reverse Cutting Needle: This needle features a curved body and a reverse cutting point, making it suitable for skin closure in recessed areas or curved incisions.
-
Half-Circle Cutting Needle: This needle features a shallow curvature and a reverse cutting point, ideal for suturing skin on convex surfaces.
Conclusion
Suture needles, in their intricate designs and diverse applications, stand as indispensable companions to sutures in the realm of wound closure. Understanding the interplay between suture needle selection, skin characteristics, and wound type is crucial for achieving optimal healing outcomes. As surgical techniques continue to evolve, suture needles are constantly being refined, ensuring that surgeons have the tools they need to meticulously repair and restore the human body.
Post time: 11月-27-2023